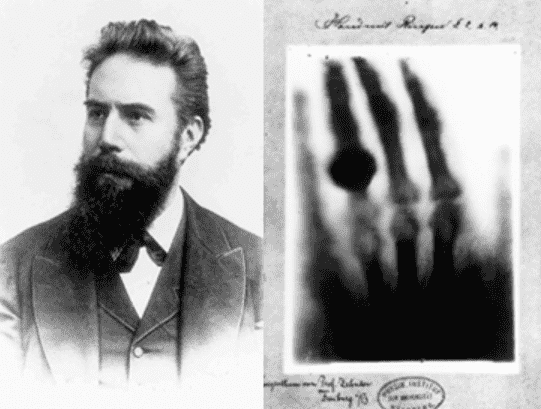
What is radiation?
X-ray system
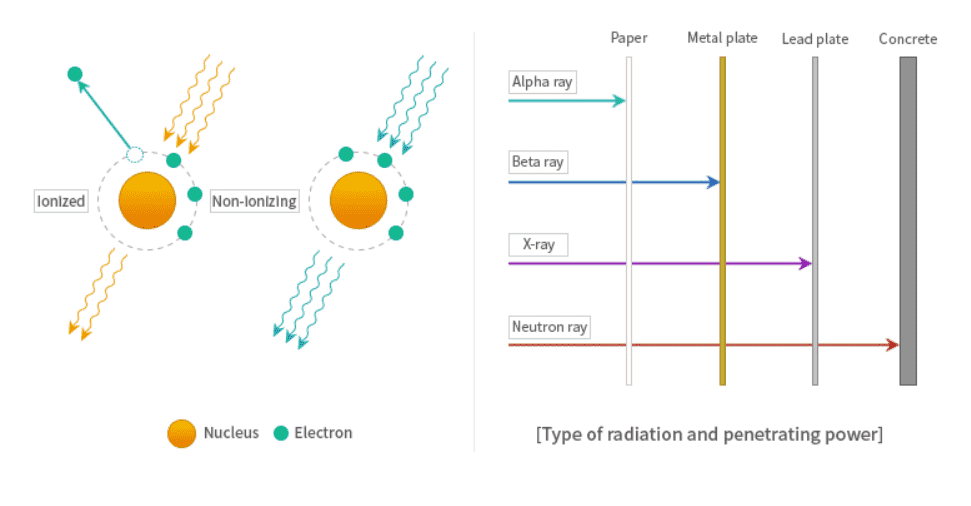
- Ionized radiation : Radiation causes ionization shooting orbital electron of atom outward
Alpha particle, beta particle, neutron, electron, proton, gamma ray, X-ray etc.
- Non-ionizing radiation : Radiation does not cause ionization
Sunray, ultraviolet, infrared ray, visible ray etc.
What is X-ray?
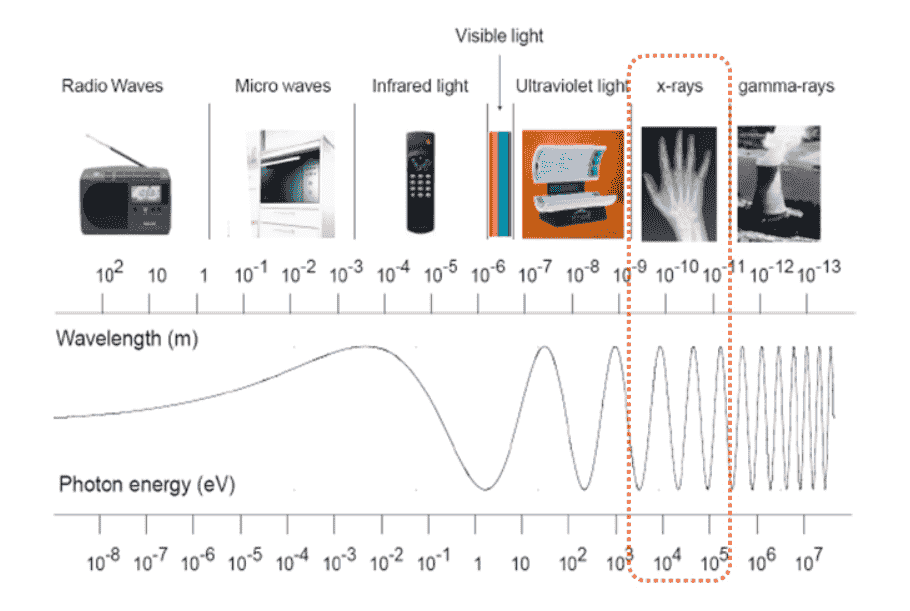
- Electronic wave at 10-11~10-9m wavelength
- Strong penetrating power into material surface
- Utilized as non-destructive inspection such as medical equipment and
industrial inspection system by using differentiation of penetrating power
Characteristic of X-ray
- Photograph action
- Fluorescence effect – make fluorescence when expose to ZnS, CdS, NaI etc.
- Ionization effect
- High rate penetration
- Same speed as light in vacuum
- Diffraction
- The refraction rate is almost 1.
Principle of X-ray Generation
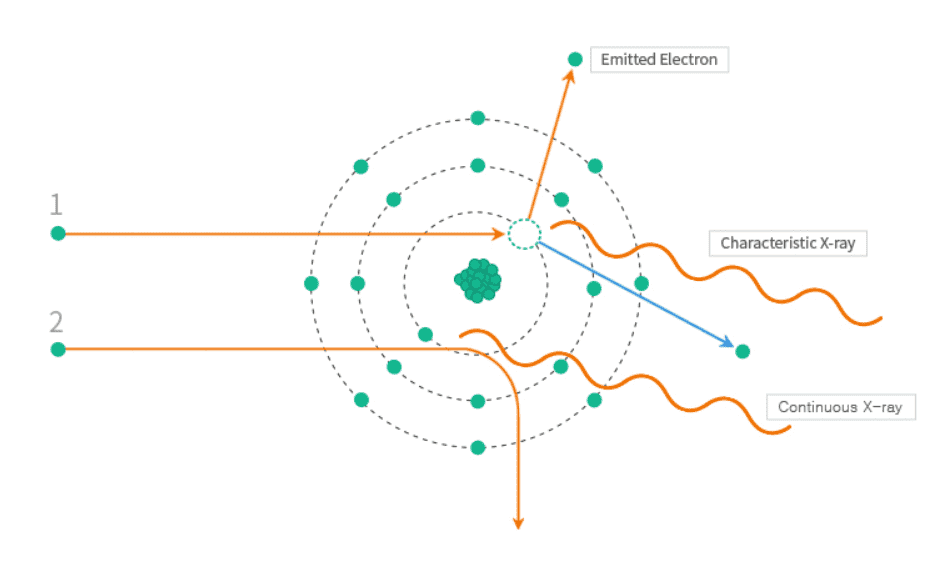
Characteristic X-ray : Accelerated electron interacts with orbital electron and outside electron is transferred.
Electric wave is emitted as the difference of energy and the wave is called characteristic X-ray.
Continuous X-ray : Accelerated electron is decelerated buy the Coulomb Potential Energy around a nucleus, and emits radiation as much as decelerated difference. This is called bremsstrahlung ray or continuous X-ray.
X-ray System
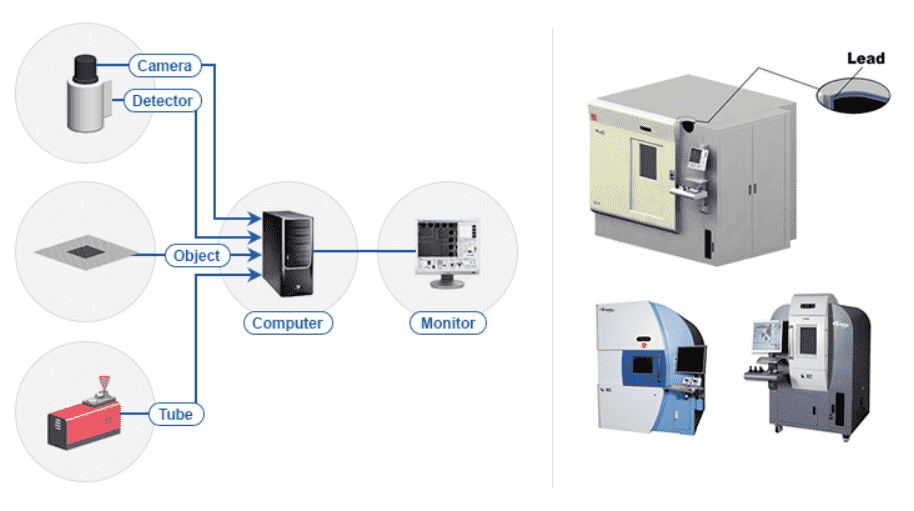
| X-ray Tube | Generates X-ray |
| Table | Moves sample in radiation equipment |
| Detector | Converts transmission electron to visible light |
| CCD Camera | Converts visible light from Detector to digital data |
| Controller | Controls image and entire system of inspection system |
| Shield cabinet | Shields radiation |
Advantage of X-ray Inspection
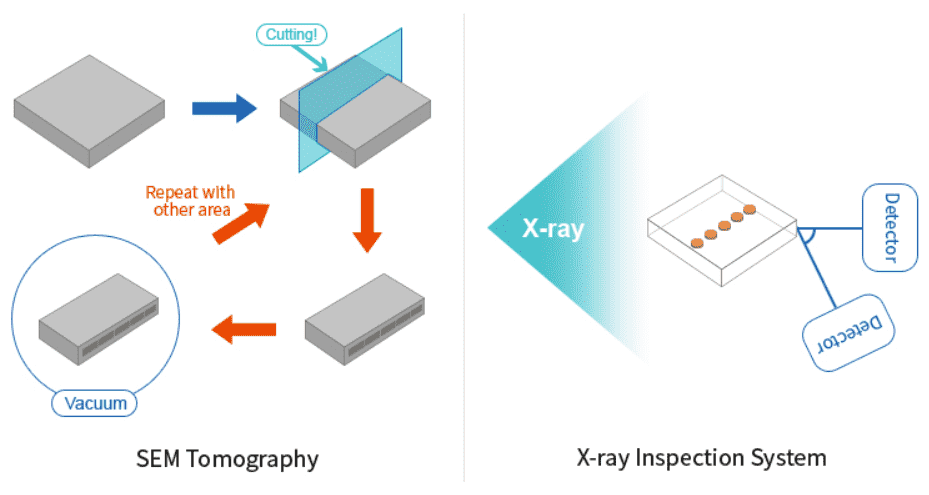
-
No need Vacuum unlike SEM
- Non-destructive inspection by using high penetrating power
No need preprocessing(cutting, destroying) for inside inspection - Simple inspection process and easy to operate
See more for SEC X-ray
Types of X-ray Tube
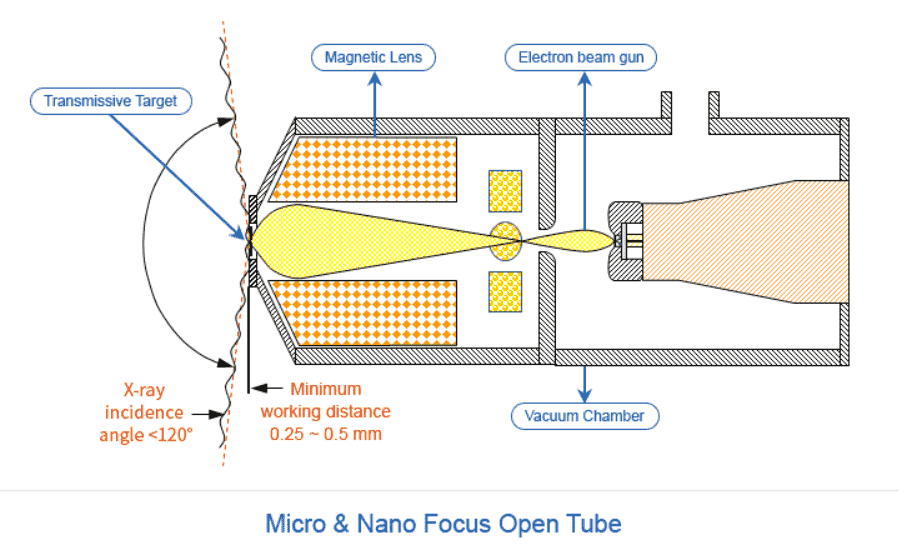
Open Tube
Vacuum condition can be built from pump installed system
Higher magnification and resolution than Closed tube
Consumables(Target, Filament etc.) are replaceable and semi-permanent
Representative models are X-eye SF160FCT and X-eye 7000B.
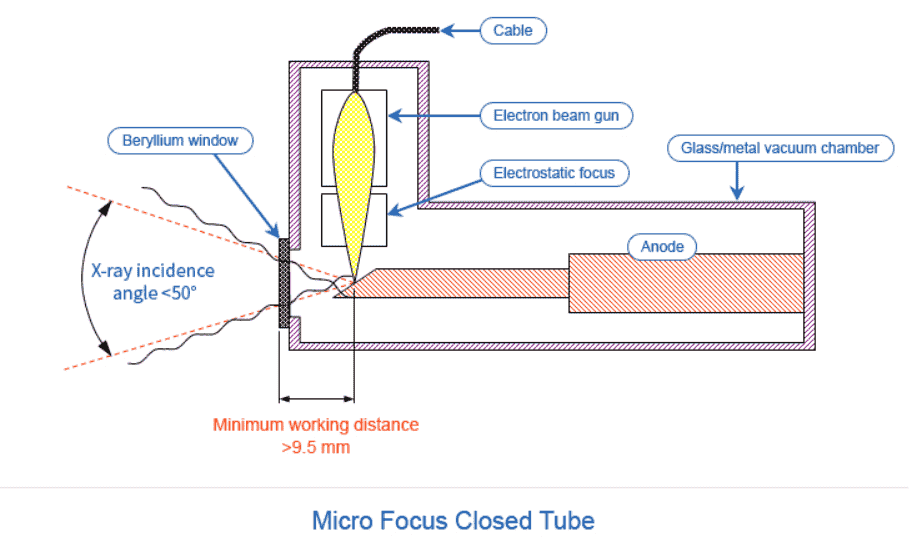
Closed Tube
Vacuum condition sealed during manufacturing process
Unable to replace inside components
Change every set if broken
Representative models are X-eye 5100F and X-eye 5000N.
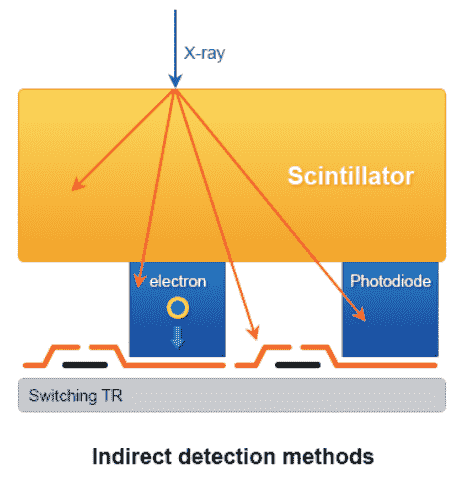
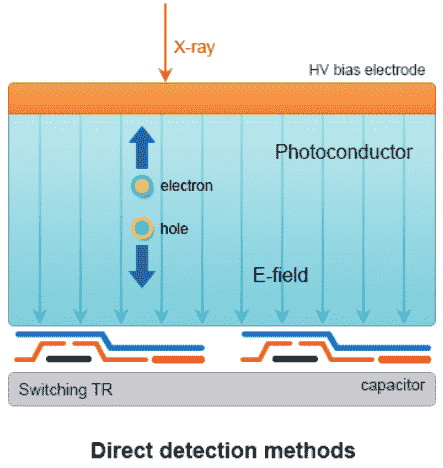
Types of X-ray Detector
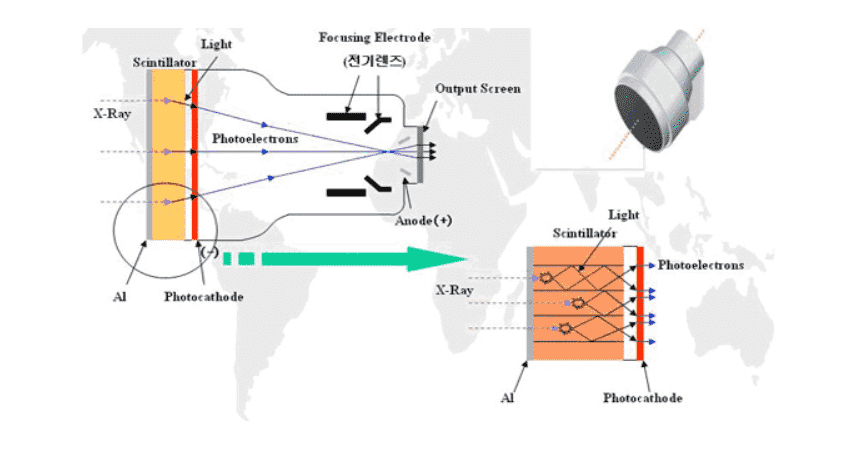
- X-ray system is converted to visible light when absorbed by Scintillator through Al
- Input window (high transmission and low diffusion of X-ray system)
- Visible light is converted to photoelectron image by Photocathode
- Photoelectron is accelerated by DC voltage
- Focused by Focusing Electrode
- Convert photoelectron image to visible ray again
|
|
Image Intensifier |
FPD |
Remark |
|
Principle |
X-ray > Input phosphor (CsI) > Amplification > Output phosphor > Visible ray > Digital Camera Integration |
X-ray > Input phosphor (CsI) > Visible ray > Camera Integration |
– |
|
Sensor |
CCD Camera Integration |
Cmos Sensor |
Decide difference of color sense and quality |
|
Resolution |
11 Lp/mm |
8 Lp/mm |
Decide image definition |
|
Frame rate |
30 ~ 48 f/s |
4 ~ 8 f/s |
Decide scanning speed |
|
Distortion rate |
Approx. 3% |
Approx. 0% |
Decide image distortion |
|
Installation place |
Large space |
Small space |
Decide System construction |
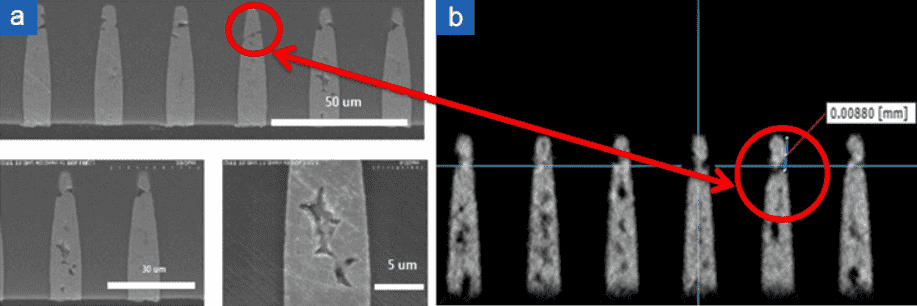
Focal spot size
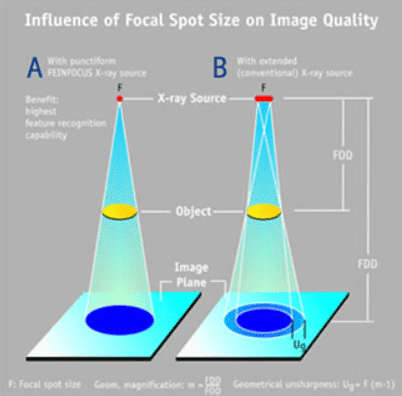 |
– The point electron colliding to Target
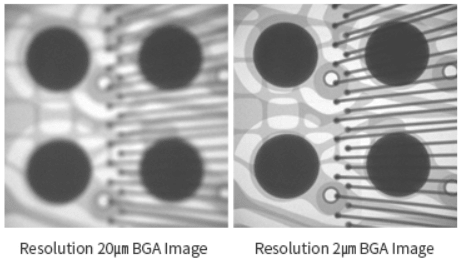
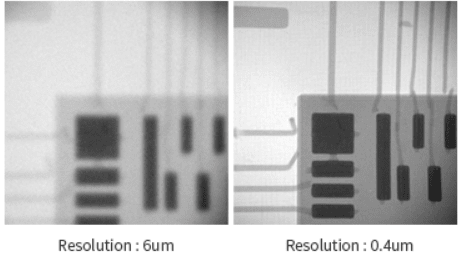
– Diameter of Focal Spot decides resolution. Smaller Focal spot size, better resolution. |
 |
 |